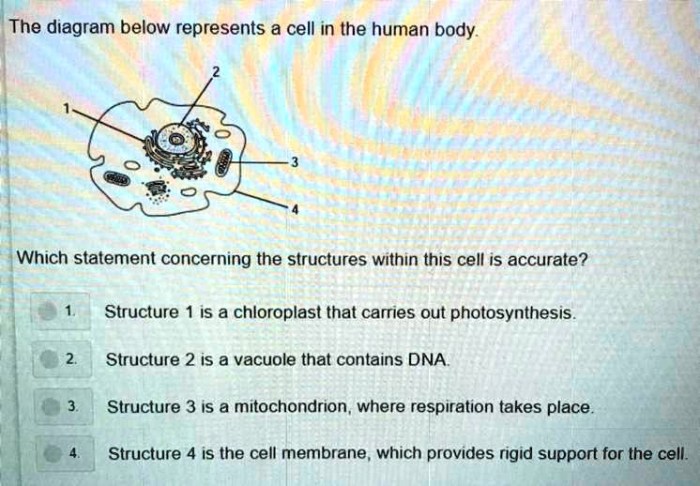
Which statement concerning the structures within this cell is accurate? This question delves into the intricate world of cellular biology, where we explore the diverse components that orchestrate the symphony of life. From the nucleus, the control center of the cell, to the mitochondria, the energy powerhouses, each organelle plays a vital role in maintaining cellular homeostasis and ensuring the proper functioning of the organism.
The cell membrane, a selectively permeable barrier, regulates the exchange of substances between the cell and its surroundings, while the cytosol, the jelly-like substance that fills the cell, provides a medium for various biochemical reactions.
Structural Features of the Cell: Which Statement Concerning The Structures Within This Cell Is Accurate
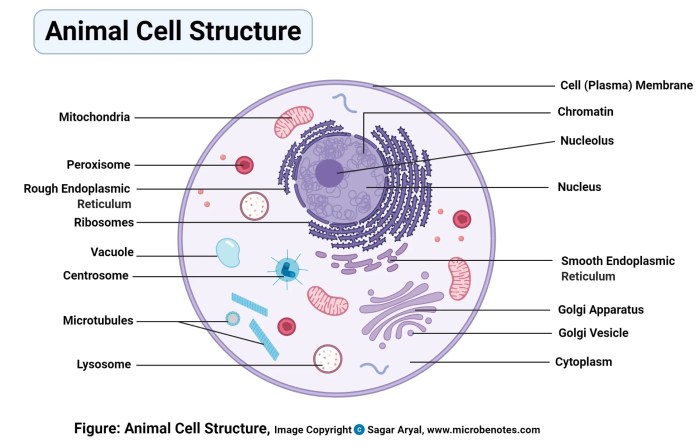
Cells, the fundamental units of life, possess a remarkable array of internal structures that facilitate their diverse functions. These structures, collectively known as organelles, are responsible for carrying out specific cellular processes and maintaining cellular integrity.
The cell membrane, a thin, semipermeable barrier, encloses the cell and regulates the passage of substances into and out of the cell. It maintains cellular homeostasis by controlling the movement of molecules and ions across the membrane.
The cytosol, the fluid-filled interior of the cell, contains a complex mixture of proteins, carbohydrates, lipids, and ions. It is the site of numerous biochemical reactions and cellular processes.
Organelles and Their Functions, Which statement concerning the structures within this cell is accurate
The nucleus, the control center of the cell, houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA. It is surrounded by a nuclear envelope, which regulates the exchange of materials between the nucleus and the cytosol.
Mitochondria, often referred to as the “powerhouses of the cell,” are responsible for generating energy through cellular respiration. They convert glucose into ATP, the primary energy currency of the cell.
The endoplasmic reticulum (ER) is a network of interconnected membranes that plays a crucial role in protein synthesis and modification. The Golgi apparatus, located near the ER, further modifies and packages proteins before they are released from the cell.
Lysosomes, small organelles containing digestive enzymes, function as the cell’s waste disposal system. They break down and recycle cellular waste, including damaged organelles and proteins.
Cytoskeleton and Cell Shape
The cytoskeleton, a dynamic network of protein filaments, provides structural support and shape to the cell. It consists of microtubules, microfilaments, and intermediate filaments.
Microtubules, the thickest cytoskeletal filaments, are responsible for maintaining cell shape, facilitating cell movement, and organizing the cell’s internal structures.
Microfilaments, the thinnest cytoskeletal filaments, play a critical role in cell movement, including cell crawling and phagocytosis. They also provide structural support to the cell.
Intermediate filaments, which are intermediate in size between microtubules and microfilaments, contribute to the cell’s mechanical stability and shape. They are found in the nuclear lamina, which supports the nuclear envelope.
Cell-Cell Interactions
Cells do not exist in isolation but interact with each other and their surrounding environment. Cell adhesion molecules (CAMs) mediate these interactions by binding to CAMs on adjacent cells.
Gap junctions, channels that connect adjacent cells, allow for the direct exchange of ions, molecules, and electrical signals between cells. This facilitates rapid intercellular communication.
Plasmodesmata, channels that connect adjacent plant cells, serve a similar function to gap junctions. They allow for the exchange of molecules and nutrients between plant cells.
Cell signaling, the process by which cells communicate with each other, is essential for coordinating cellular activities. Cells release signaling molecules that bind to receptors on target cells, triggering specific cellular responses.
Common Queries
What is the function of the nucleus?
The nucleus houses the cell’s genetic material, DNA, and controls cellular activities.
What is the role of mitochondria in the cell?
Mitochondria are responsible for energy production through cellular respiration.
What is the function of the endoplasmic reticulum?
The endoplasmic reticulum is involved in protein synthesis, lipid metabolism, and detoxification.