Welcome to the realm of cellular respiration, where the intricate dance of life unfolds. Cellular respiration biology corner answer key unveils the mysteries of this vital process, providing a comprehensive guide to understanding how cells generate the energy they need to thrive.
Delve into the depths of glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, and the electron transport chain, exploring the intricate mechanisms that orchestrate the conversion of glucose into ATP, the universal energy currency of life.
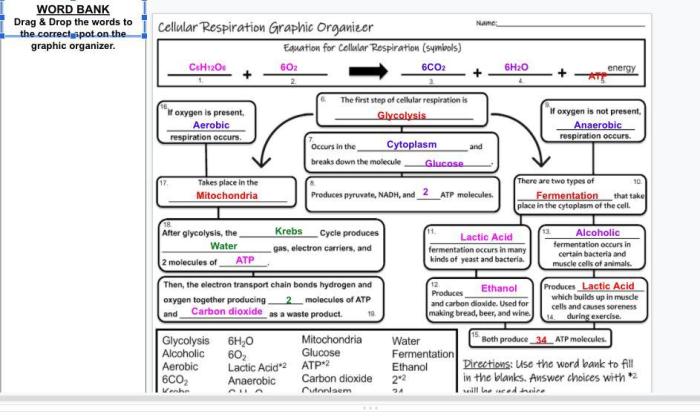
Cellular Respiration
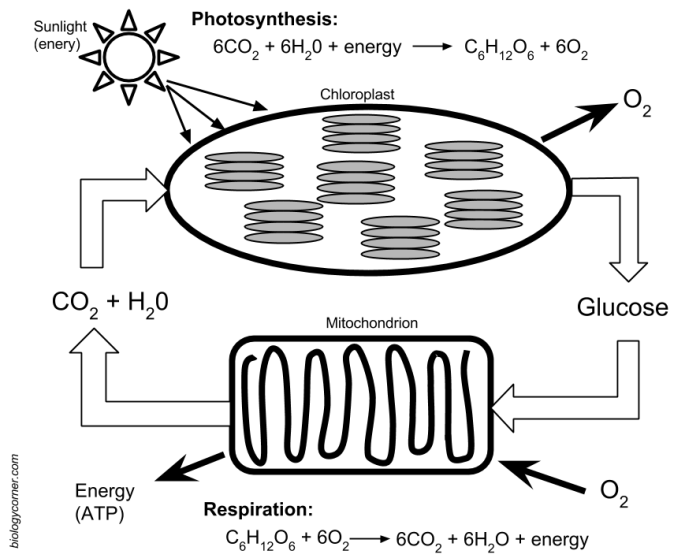
Cellular respiration is a set of metabolic reactions that take place in the cells of organisms to convert biochemical energy from nutrients into adenosine triphosphate (ATP), and then release waste products. This process is essential for the survival of all living organisms because ATP serves as the main energy currency for cells.
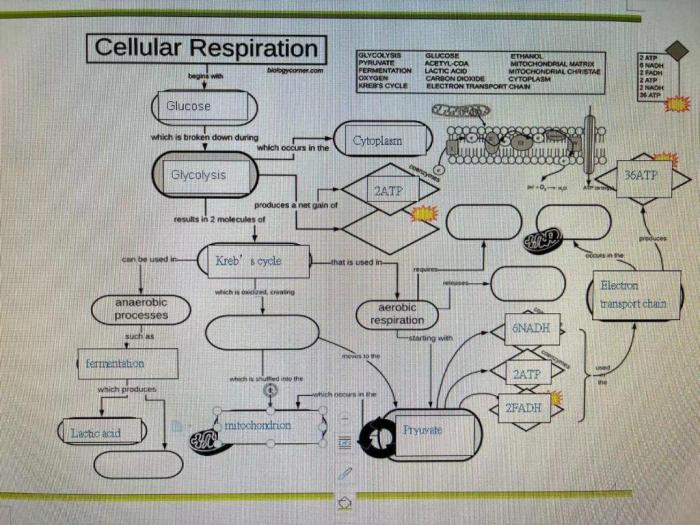
Cellular respiration can be divided into four main stages: glycolysis, the Krebs cycle, the electron transport chain, and oxidative phosphorylation. Each stage plays a specific role in the overall process of energy production.
Glycolysis
Glycolysis is the first stage of cellular respiration and occurs in the cytoplasm of the cell. During glycolysis, one molecule of glucose is broken down into two molecules of pyruvate, along with a net gain of two molecules of ATP and two molecules of NADH.
Krebs Cycle (Citric Acid Cycle)
The Krebs cycle takes place in the mitochondria of the cell and is a series of chemical reactions that further break down pyruvate into carbon dioxide. During the Krebs cycle, a net of two molecules of ATP, six molecules of NADH, and two molecules of FADH2 are produced.
Electron Transport Chain
The electron transport chain is a series of protein complexes located in the inner membrane of the mitochondria. During the electron transport chain, NADH and FADH2 molecules produced in glycolysis and the Krebs cycle are used to generate ATP through a process called oxidative phosphorylation.
Regulation of Cellular Respiration, Cellular respiration biology corner answer key
Cellular respiration is a tightly regulated process to ensure that the cell’s energy needs are met. The rate of cellular respiration is controlled by a number of factors, including the availability of oxygen, the levels of ATP and ADP, and the activity of various enzymes.
Anaerobic Respiration
Anaerobic respiration is a type of cellular respiration that occurs in the absence of oxygen. During anaerobic respiration, glucose is broken down into lactic acid or ethanol, along with a net gain of two molecules of ATP.
Importance of Cellular Respiration
Cellular respiration is essential for the survival of all living organisms. It provides the energy that cells need to carry out their various functions, such as growth, reproduction, and movement. Without cellular respiration, cells would not be able to function and organisms would not be able to survive.
FAQ Summary: Cellular Respiration Biology Corner Answer Key
What is the significance of cellular respiration?
Cellular respiration is essential for life, providing the energy required for cellular processes such as growth, movement, and reproduction.
Where does glycolysis take place?
Glycolysis occurs in the cytoplasm of cells.
How many ATP molecules are produced during the Krebs cycle?
The Krebs cycle generates 2 ATP molecules per glucose molecule.