Identify the polynomial. a 2 + b – cd 3 – Polynomials, represented by expressions like a^2 + b – cd^3, form the cornerstone of mathematical analysis. This polynomial, a^2 + b – cd^3, serves as a prime example for understanding the fundamental concepts of polynomials, their operations, and their diverse applications.
Delving into the intricacies of this polynomial, we will explore its individual terms, coefficients, and degrees, gaining insights into the significance of polynomial analysis in various scientific and practical domains.
Polynomial Basics
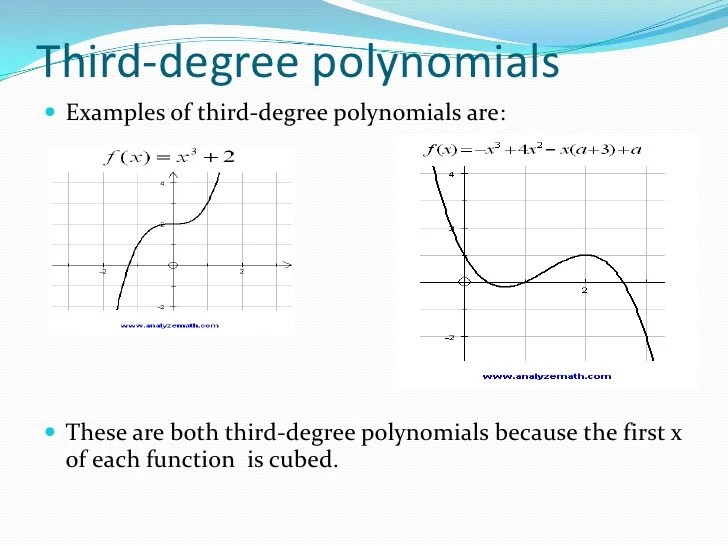
A polynomial is a mathematical expression that consists of a sum of terms, each of which is a product of a coefficient and a variable raised to a non-negative integer power. Polynomials are widely used in various fields, including algebra, calculus, and statistics.
Polynomials are characterized by their terms, coefficients, and degrees. A term is a single product of a coefficient and a variable raised to a power. The coefficient is a constant value that multiplies the variable. The degree of a term is the exponent of the variable.
The degree of a polynomial is the highest degree of any of its terms. Polynomials can be classified into different types based on their degree, such as linear polynomials (degree 1), quadratic polynomials (degree 2), cubic polynomials (degree 3), and so on.
Identifying the Polynomial: a^2 + b
cd^3
cd^3
The polynomial a^2 + b – cd^3 consists of three terms: a^2, b, and -cd^3. The coefficients of these terms are 1, 1, and -c, respectively. The degrees of these terms are 2, 0, and 3, respectively.
The degree of the polynomial is the highest degree of any of its terms, which in this case is 3. Therefore, a^2 + b – cd^3 is a cubic polynomial.
Polynomial Operations, Identify the polynomial. a 2 + b – cd 3
Polynomials can be manipulated using basic operations such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication. These operations follow the usual rules of algebra, but there are some important considerations when working with polynomials.
When adding or subtracting polynomials, the like terms are combined. Like terms are terms that have the same variable raised to the same power. For example, in the polynomials a^2 + b and 2a^2 – b, the like terms are a^2 and -b, which can be combined to give 3a^2.
When multiplying polynomials, the distributive property is used to multiply each term of one polynomial by each term of the other polynomial. For example, in the polynomials (a + b)(a – b), the terms are multiplied as follows:
- (a)(a) = a^2
- (a)(b) = ab
- (b)(a) = ab
- (b)(b) = b^2
The resulting polynomial is a^2 – b^2.
Polynomial Applications
Polynomials have numerous applications in various fields, including:
- Modeling:Polynomials can be used to model real-world phenomena, such as the trajectory of a projectile or the growth of a population.
- Problem-solving:Polynomials can be used to solve a variety of problems, such as finding the roots of an equation or optimizing a function.
- Decision-making:Polynomials can be used to make informed decisions, such as determining the optimal production level for a business or the best investment strategy.
Understanding polynomials is essential for success in many fields that involve mathematics, including science, engineering, economics, and finance.
Common Queries: Identify The Polynomial. A 2 + B – Cd 3
What is a polynomial?
A polynomial is a mathematical expression consisting of variables and coefficients, combined using algebraic operations such as addition, subtraction, and multiplication. Each term within the polynomial has a non-negative integer exponent.
What are the terms and coefficients of a polynomial?
Terms are the individual components of a polynomial, each consisting of a coefficient and a variable raised to a power. Coefficients are the numerical factors that multiply the variables.
What is the degree of a polynomial?
The degree of a polynomial is the highest exponent of any variable in the polynomial. It determines the overall complexity and behavior of the polynomial.