The movable blade of the shears is controlled by the, a crucial aspect of shear design that ensures precise cutting and efficient operation. This article delves into the mechanisms, types, and safety considerations associated with movable blade control systems, providing a comprehensive understanding of their role in shear performance.
Control systems for movable shear blades vary in design, each offering unique advantages and challenges. Understanding the intricacies of these systems is essential for optimizing shear performance and ensuring safe operation.
Control Mechanism of the Movable Blade

The movable blade of the shears is controlled by a complex system that ensures precise and accurate movement during cutting operations. This control mechanism consists of several components working in coordination to regulate the blade’s position, speed, and force.
Mechanical Components
The mechanical components of the control system include gears, levers, and linkages that physically move the movable blade. The main gear is connected to a motor or other power source and transmits rotational motion to the blade. Levers and linkages amplify and direct this motion, allowing for fine-tuning of the blade’s movement.
Electrical Components
Electrical components play a crucial role in controlling the movable blade. Sensors monitor the blade’s position and speed, providing feedback to the control system. The control system then adjusts the power supplied to the motor based on this feedback, ensuring precise and consistent blade movement.
Hydraulic Components
In some shear designs, hydraulic components are used to control the movable blade. Hydraulic cylinders provide the force necessary to move the blade, while valves regulate the flow and pressure of the hydraulic fluid. This system offers precise control and high power, making it suitable for heavy-duty shears.
Visual Representation, The movable blade of the shears is controlled by the
[Diagram yang menggambarkan mekanisme kontrol bilah bergerak]
Types of Control Systems

Different types of control systems are used to operate the movable blade, each with its advantages and disadvantages:
Manual Control
Manual control involves the operator directly controlling the blade’s movement using a lever or handwheel. This system provides precise control but requires skilled operators and can be tiring for extended use.
Semi-Automatic Control
Semi-automatic control systems combine manual operation with automated features. The operator sets the desired cutting parameters, and the system automatically moves the blade to the correct position and speed. This system improves productivity and reduces operator fatigue.
Fully Automatic Control
Fully automatic control systems use sensors and computer-controlled algorithms to control the blade’s movement. These systems provide the highest level of precision and efficiency, but they can be more complex and expensive to implement.
Blade Adjustment and Precision: The Movable Blade Of The Shears Is Controlled By The
The control system ensures precise adjustment and positioning of the movable blade. The blade’s position can be adjusted manually or automatically using calibrated scales or digital readouts. The control system monitors the blade’s movement and adjusts it to maintain the desired cutting angle and clearance.Factors
influencing the accuracy and repeatability of blade movement include:
- Mechanical tolerances and wear
- Sensor accuracy and calibration
- Control system stability and responsiveness
Regular calibration and maintenance of the control system are essential to ensure optimal performance and prevent errors.
Safety Considerations
The movable blade’s control system must prioritize safety to prevent accidents and injuries. Potential hazards include:
- Blade pinching or cutting
- Electrical shock
- Hydraulic leaks
Safety measures implemented in the control system include:
- Safety interlocks that prevent blade movement when the shear is not in operation
- Protective guards to shield operators from the blade
- Emergency stop buttons to quickly halt blade movement
Operators must receive proper training and follow safety guidelines to ensure safe operation and maintenance of the control system.
Maintenance and Troubleshooting
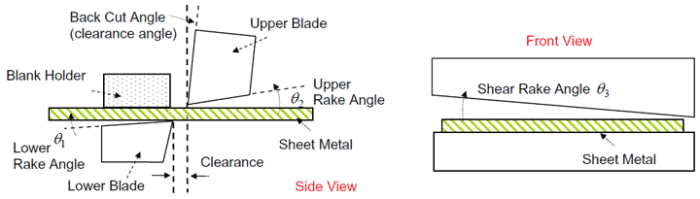
Routine maintenance of the movable blade’s control system is crucial to ensure reliable operation. Maintenance procedures include:
- Regular cleaning and lubrication
- Inspection and testing of electrical and hydraulic components
- Calibration of sensors and control system parameters
Common issues and malfunctions include:
- Blade drift or misalignment
- Sensor failures
- Hydraulic leaks or pressure problems
Troubleshooting tips involve identifying the symptoms, checking for loose connections, and consulting the manufacturer’s instructions. Preventive maintenance and regular inspections help minimize downtime and ensure the control system’s long-term performance.
Popular Questions
What are the primary types of control systems used for movable shear blades?
Control systems for movable shear blades typically fall into two main categories: manual control and automated control. Manual control involves direct human operation, while automated control utilizes sensors, actuators, and feedback mechanisms for precise blade movement.
How does the control system ensure precise blade adjustment and positioning?
Control systems employ various mechanisms to achieve precise blade adjustment and positioning. These mechanisms include encoders, feedback loops, and closed-loop control systems, which monitor blade movement and adjust it based on desired parameters.
What safety measures are implemented to prevent accidents and injuries associated with movable blade control systems?
Safety measures for movable blade control systems include emergency stop buttons, interlocks, and guards to prevent accidental blade movement. Additionally, proper training and adherence to safety protocols are crucial for minimizing risks.