Draw the salt produced in this reaction. include charges – In this in-depth exploration, we embark on a journey to decipher the intricacies of salt formation, elucidating the chemical reactions that govern their genesis. By unraveling the interplay of cations and anions, we will delineate the Lewis structures of these ionic compounds, revealing the charges that define their electrostatic interactions.
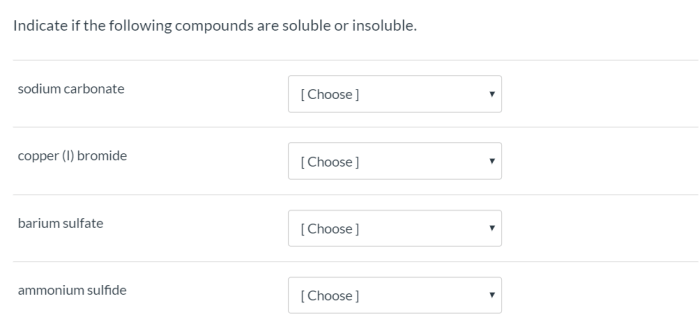
Delving deeper, we will investigate the solubility of salts in water, uncovering the factors that influence their dissolution. We will categorize salts based on their solubility and explore the physical properties that distinguish them, examining their color, shape, and texture in relation to their chemical structures.
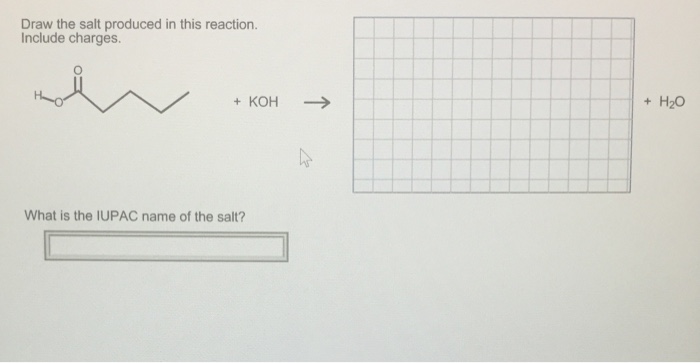
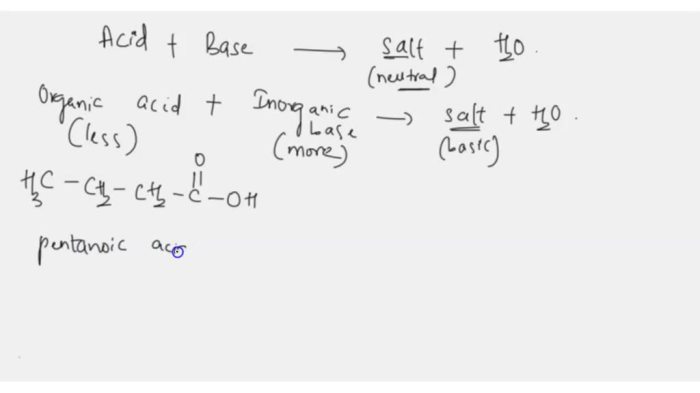
Draw the Salt Produced in this Reaction. Include Charges
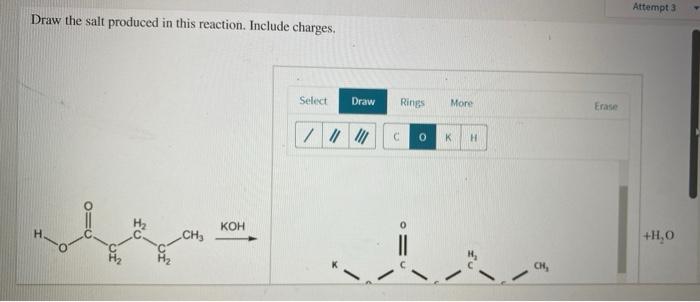
The reaction between sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrochloric acid (HCl) produces sodium chloride (NaCl), a salt. The chemical equation for this reaction is:
“`NaOH + HCl → NaCl + H 2O“`
The cations involved in this reaction are Na +and H +, while the anions are Cl –and OH –. The Lewis structure of NaCl is shown below:
“`Na +:Cl –“`
The table below summarizes the ions, their charges, and their Lewis structures:
| Ion | Charge | Lewis Structure |
|---|---|---|
| Na+ | +1 | [Ne] |
| Cl– | -1 | [Ne]3s23p6 |
FAQs
What is the difference between a cation and an anion?
Cations are positively charged ions, while anions are negatively charged ions.
How do you determine the charge of an ion?
The charge of an ion is determined by the number of electrons it has gained or lost.
What is the solubility of a salt?
The solubility of a salt is the amount of salt that can be dissolved in a given amount of water.