The Kawasaki disease nursing care plan serves as a vital guide for healthcare professionals in providing optimal care to patients with this complex condition. This plan encompasses a comprehensive approach to assessment, interventions, and patient education, ensuring the best possible outcomes for those affected by Kawasaki disease.
Kawasaki disease is a rare but serious illness that primarily affects young children. It is characterized by a wide range of symptoms, including fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, and inflammation of the blood vessels. Early diagnosis and treatment are crucial to prevent potential complications such as heart problems and coronary artery aneurysms.
Nursing Assessment: Kawasaki Disease Nursing Care Plan

Nursing assessment plays a crucial role in early identification and prompt treatment of Kawasaki disease. The nurse should be familiar with the signs and symptoms of the disease and perform a thorough physical examination.
Signs and Symptoms, Kawasaki disease nursing care plan
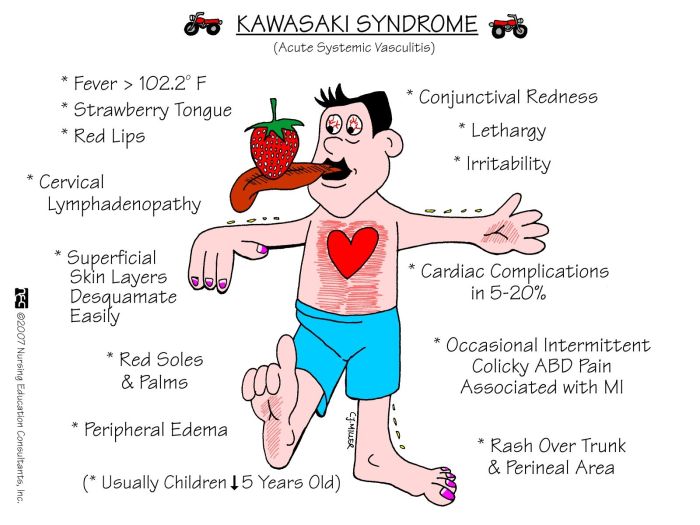
- Fever lasting more than five days
- Rash on the trunk, extremities, and perineum
- Conjunctival injection without exudate
- Erythema and swelling of the lips and oral mucosa
- Enlarged cervical lymph nodes
- Desquamation of the skin on the fingers and toes
Diagnostic Criteria
| Major Criteria | Minor Criteria |
|---|---|
| Fever lasting more than five days | Rash |
| Bilateral conjunctival injection | Changes in the lips and oral mucosa |
| Cervical lymphadenopathy | Desquamation of the skin on the fingers and toes |
Importance of Early Diagnosis and Treatment
Early diagnosis and treatment are essential to prevent the development of coronary artery complications. Treatment should be initiated within the first 10 days of illness to reduce the risk of cardiac involvement.
Nursing Interventions
Managing Fever
- Monitor temperature frequently.
- Administer antipyretics as prescribed.
- Provide tepid sponge baths to reduce fever.
- Encourage adequate hydration.
Anti-inflammatory Medications
- Administer intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) as prescribed.
- Monitor for adverse reactions to IVIG, such as fever, chills, and hypotension.
- Aspirin may be prescribed to reduce inflammation and prevent blood clots.
Monitoring Fluid Balance
- Monitor intake and output strictly.
- Administer intravenous fluids as prescribed to maintain hydration.
- Assess for signs of dehydration, such as dry mucous membranes and decreased urine output.
Nursing Care Plan

Goals
- Reduce fever and inflammation.
- Prevent cardiac complications.
- Promote comfort and well-being.
Interventions
- Monitor vital signs, including temperature, pulse, and blood pressure.
- Administer antipyretics and anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed.
- Provide tepid sponge baths to reduce fever.
- Encourage adequate hydration.
- Monitor for signs of dehydration.
- Assess for signs of cardiac involvement, such as chest pain, shortness of breath, and murmurs.
- Provide emotional support to the patient and family.
Expected Outcomes
- Fever will be reduced.
- Inflammation will be controlled.
- Cardiac complications will be prevented.
- The patient will experience improved comfort and well-being.
Nursing Care Plan Table
| Goal | Intervention | Expected Outcome |
|---|---|---|
| Reduce fever and inflammation | Administer antipyretics and anti-inflammatory medications as prescribed | Fever will be reduced |
| Prevent cardiac complications | Monitor for signs of cardiac involvement | Cardiac complications will be prevented |
| Promote comfort and well-being | Provide emotional support to the patient and family | The patient will experience improved comfort and well-being |
Answers to Common Questions
What are the common symptoms of Kawasaki disease?
Fever, rash, swollen lymph nodes, red eyes, and inflammation of the mouth, hands, and feet.
How is Kawasaki disease diagnosed?
Based on clinical symptoms and laboratory tests, including a complete blood count, erythrocyte sedimentation rate, and C-reactive protein.
What is the treatment for Kawasaki disease?
Intravenous immunoglobulin (IVIG) and aspirin are the primary treatments.
What are the potential complications of Kawasaki disease?
Heart problems, coronary artery aneurysms, and other inflammatory conditions.
What is the role of the nurse in Kawasaki disease care?
Nurses play a vital role in assessing, monitoring, educating, and providing support to patients and families throughout the course of the illness.